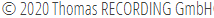Optical Fibers
Optical Fibers
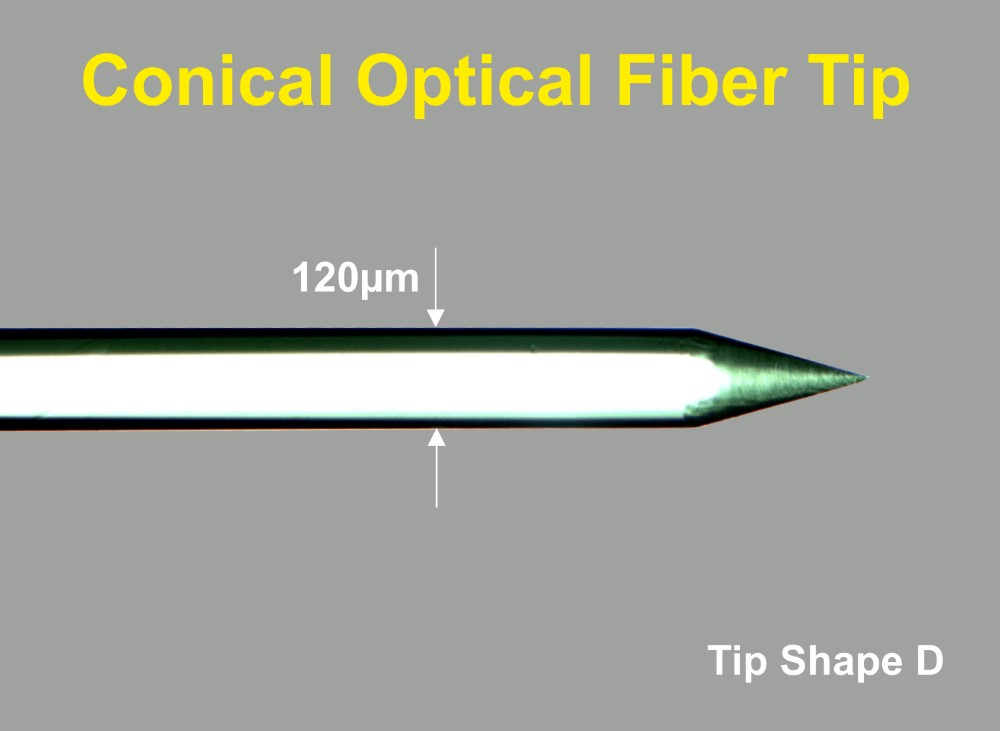
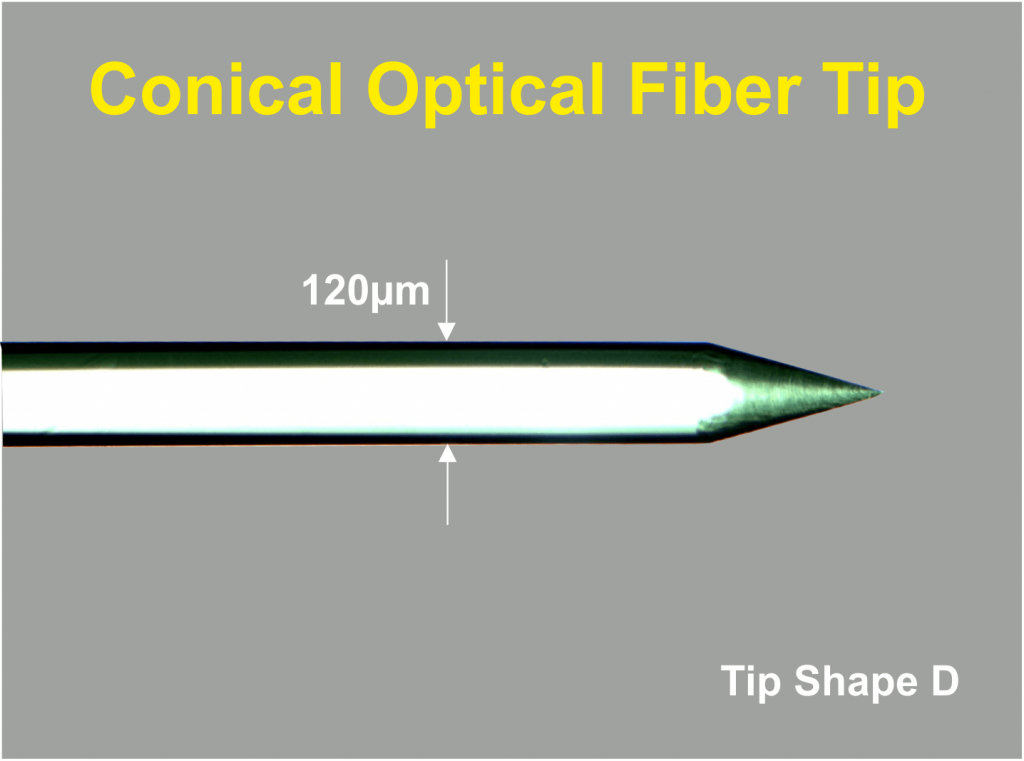
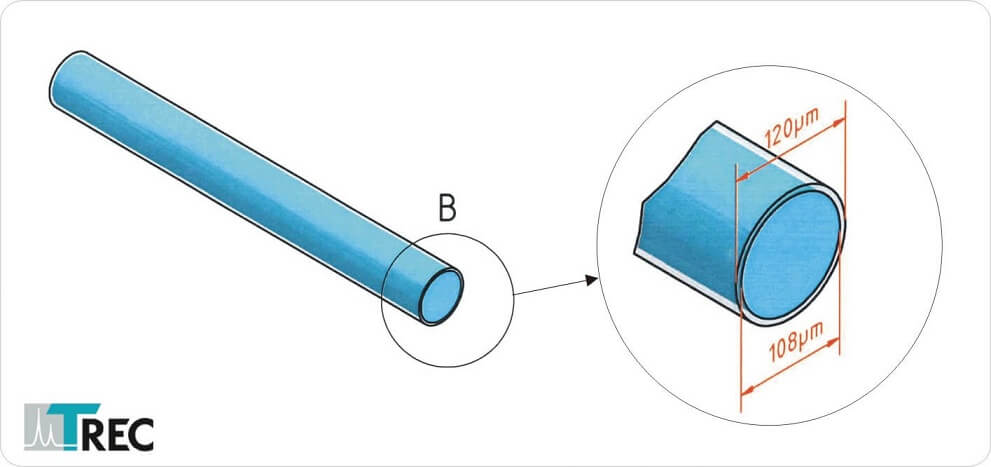
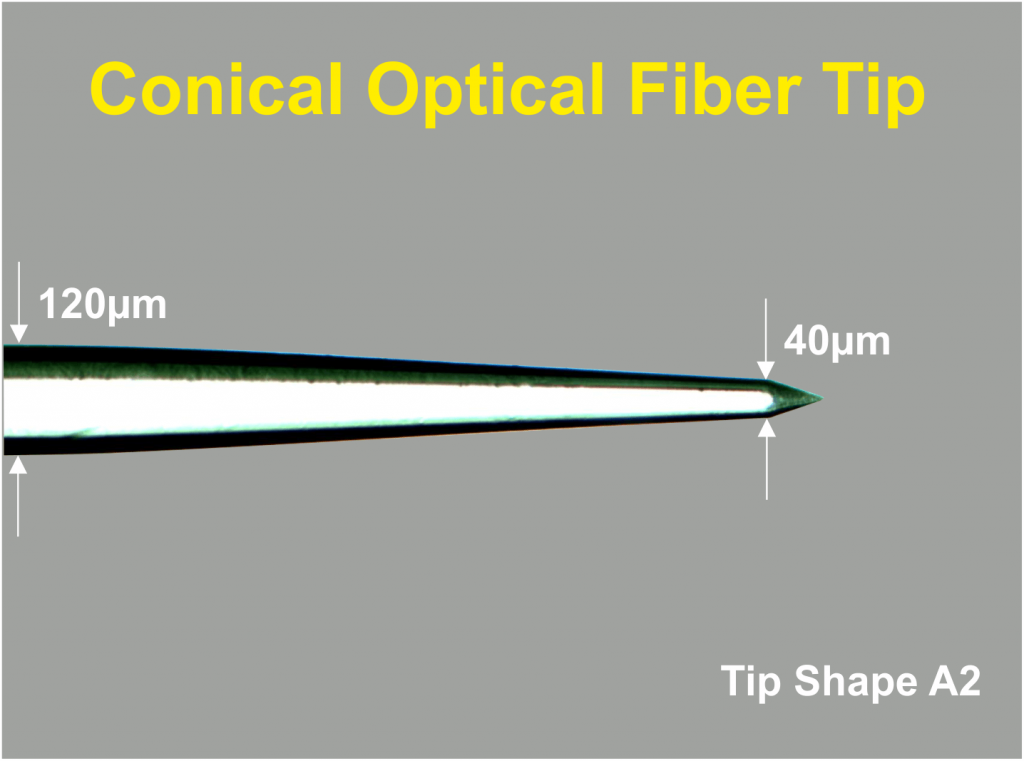
The Thomas RECORDING Optical Fibers consist of a core glass and a cladding also made of glass. The outer shaft diameter of the Optical Glass Fiber is 120µm (other diameters are available on request). The core glass has a diameter of 108µm.
- Biocompatible material
- Minimal tissue damage while introducing in brain because of double conical fibers
- Globular light distribution at the conical tip
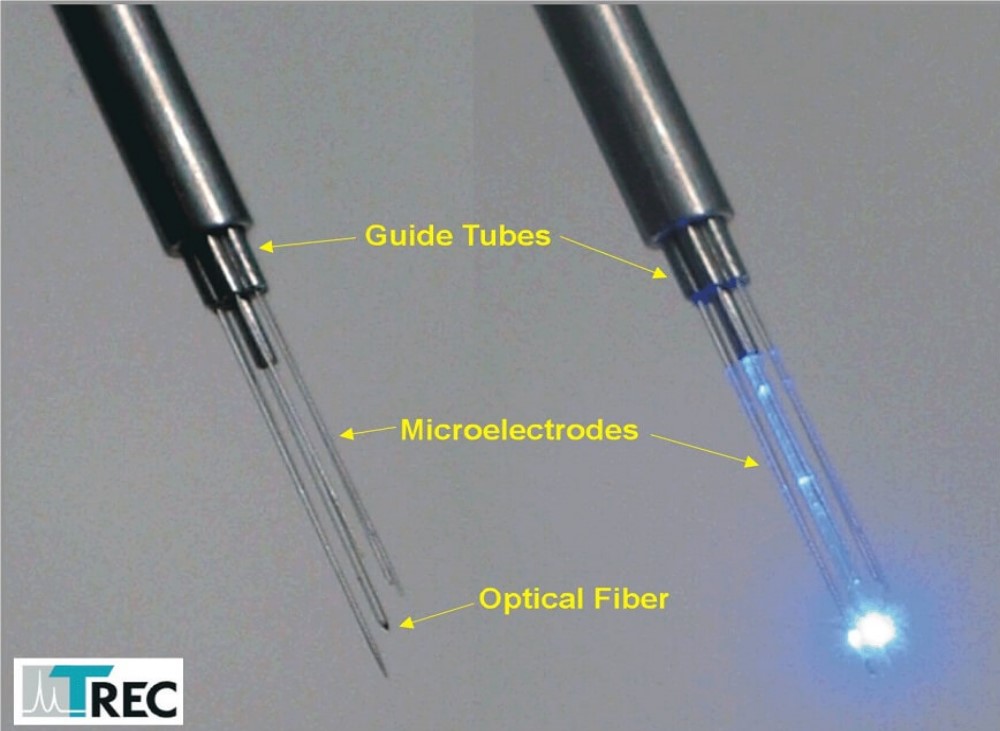
- Available for Thomas RECORDING Microdrive systems (e. g. Mini Matrix, Eckhorn Matrix) or other manipulators
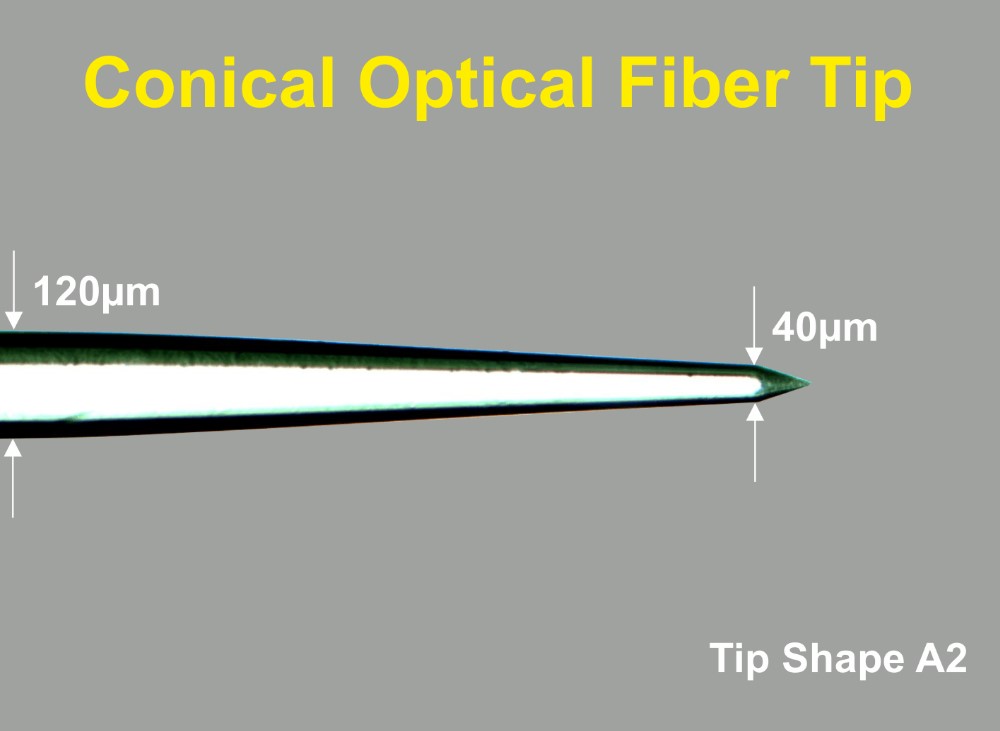
- Thomas Optical Fiber is available with differen tip shapes (Please see Figure 3)
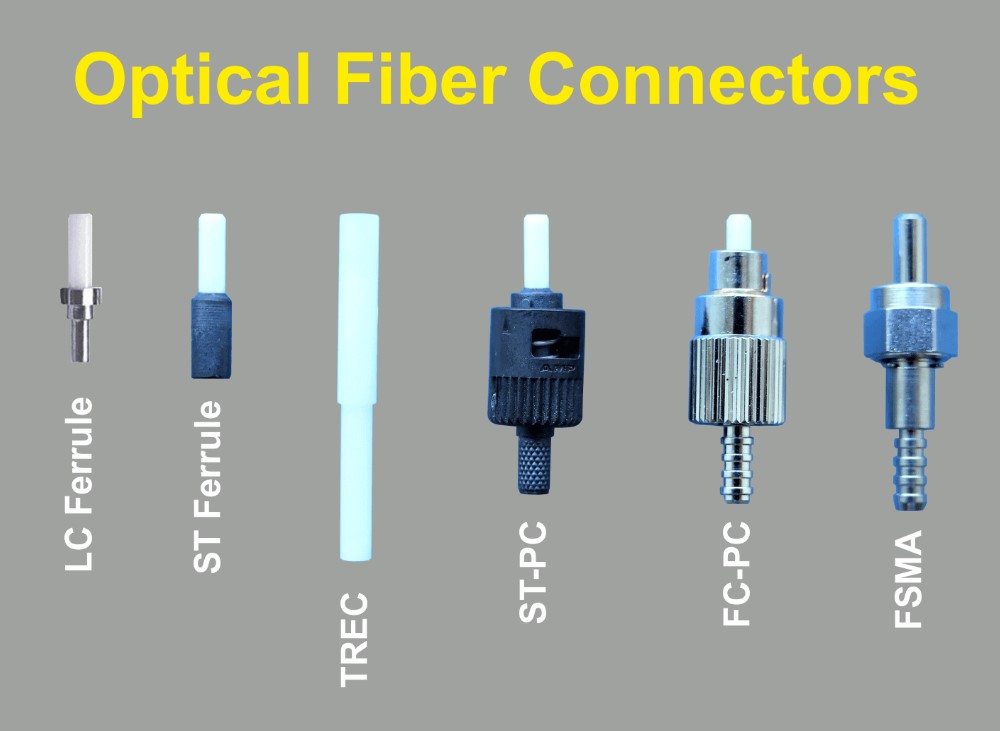
- Different fiber connectors available
| Data | |
| Material: | Optical glass |
| Outer glass fiber diameter: | 120µm |
| Available fiber tip shapes: | Conical tips, double conical tips and blunt tips |
| Article Number: | AN000514 |
Tip Types
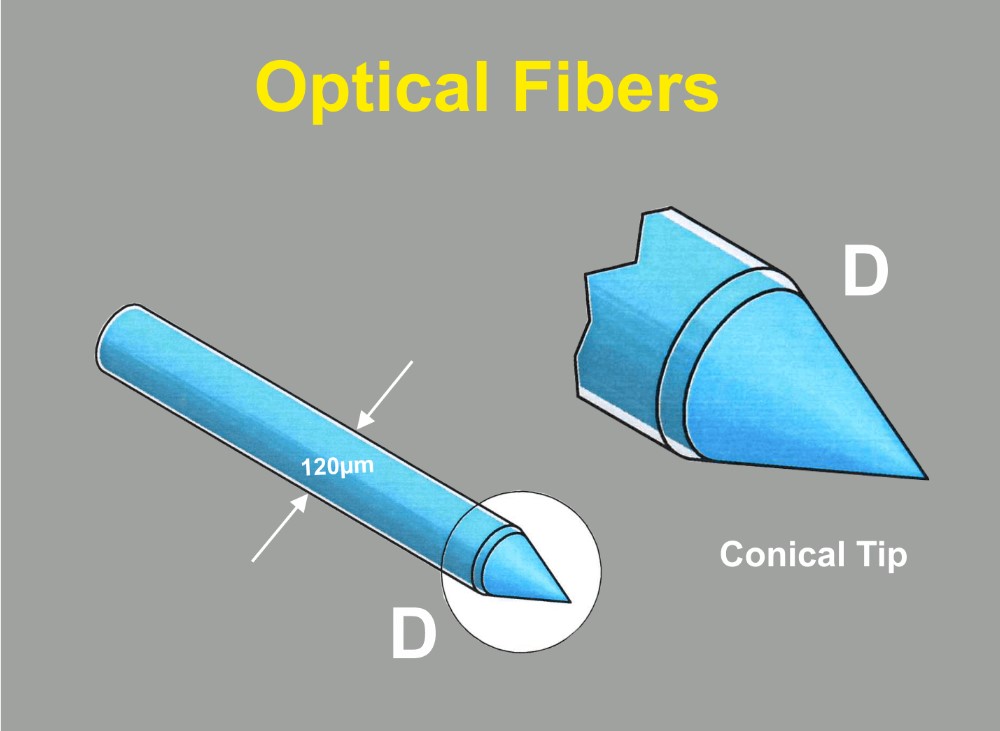
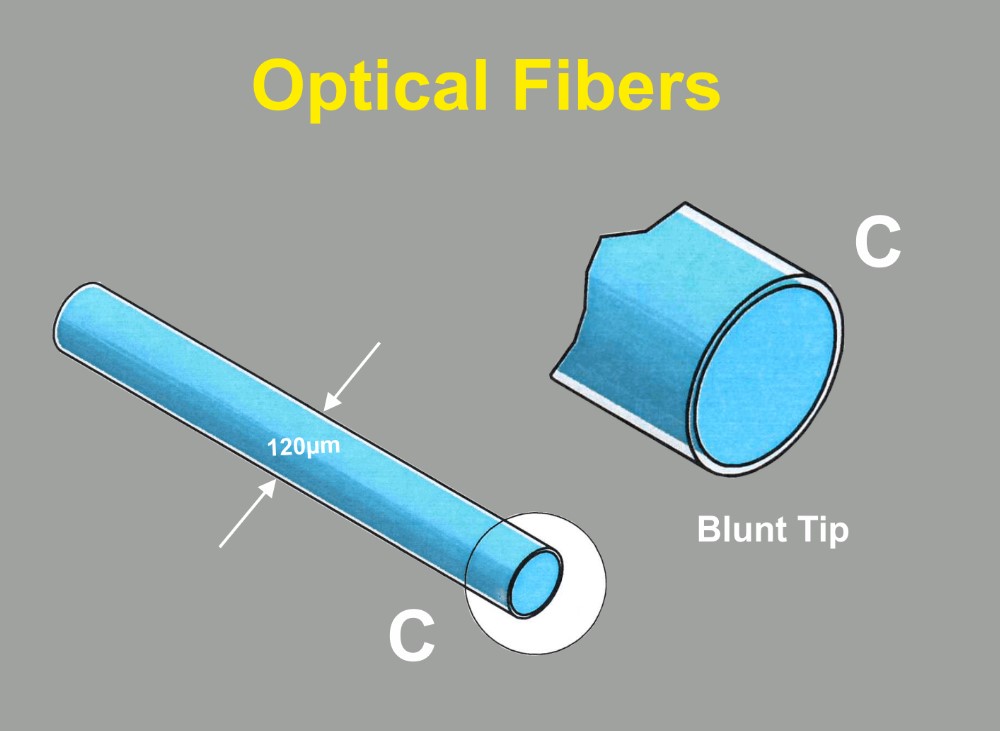
The Thomas Optical Fiber is available with blunt tip as shown in figure 1 or with a conical tip like shown in figure 2.




Tip Size
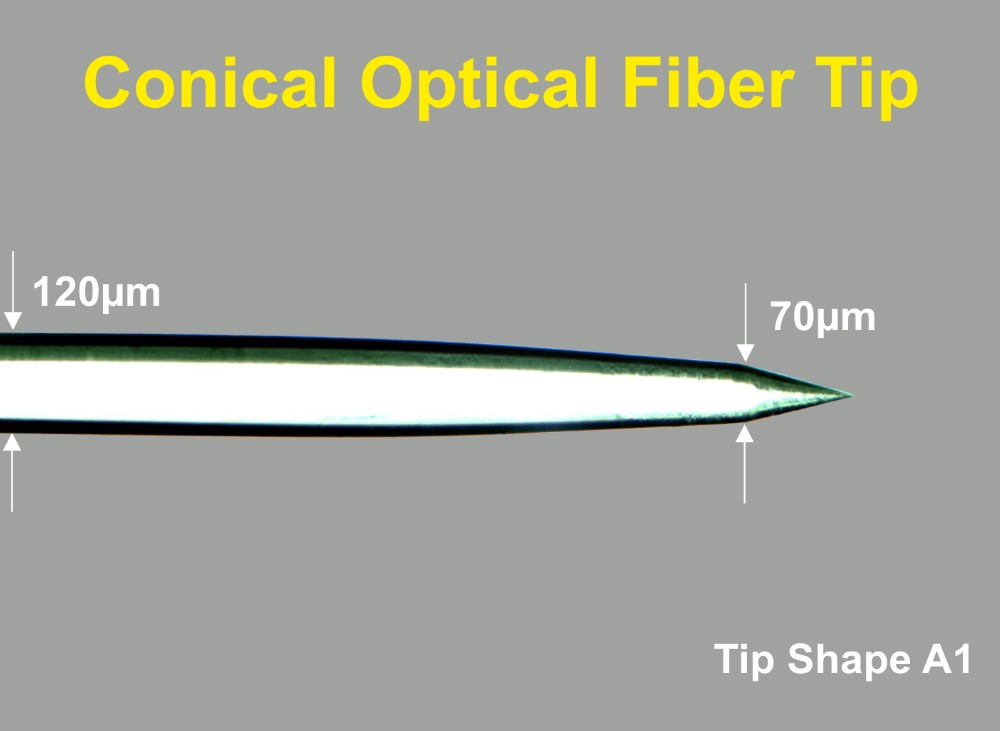
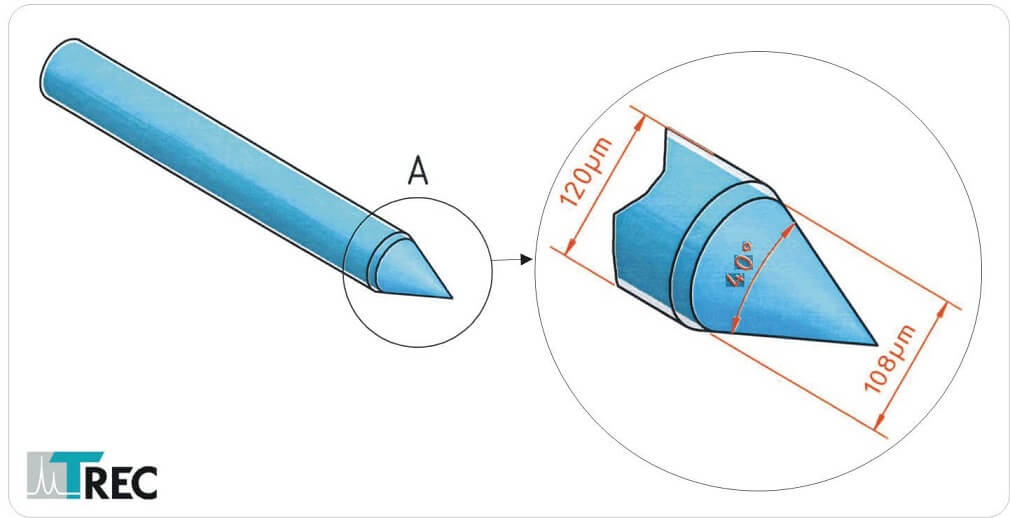
The Thomas Optical Fiber with conical tip is available in three different shapes like shown in figure 3.




Advantages of Thomas Optical Fibers
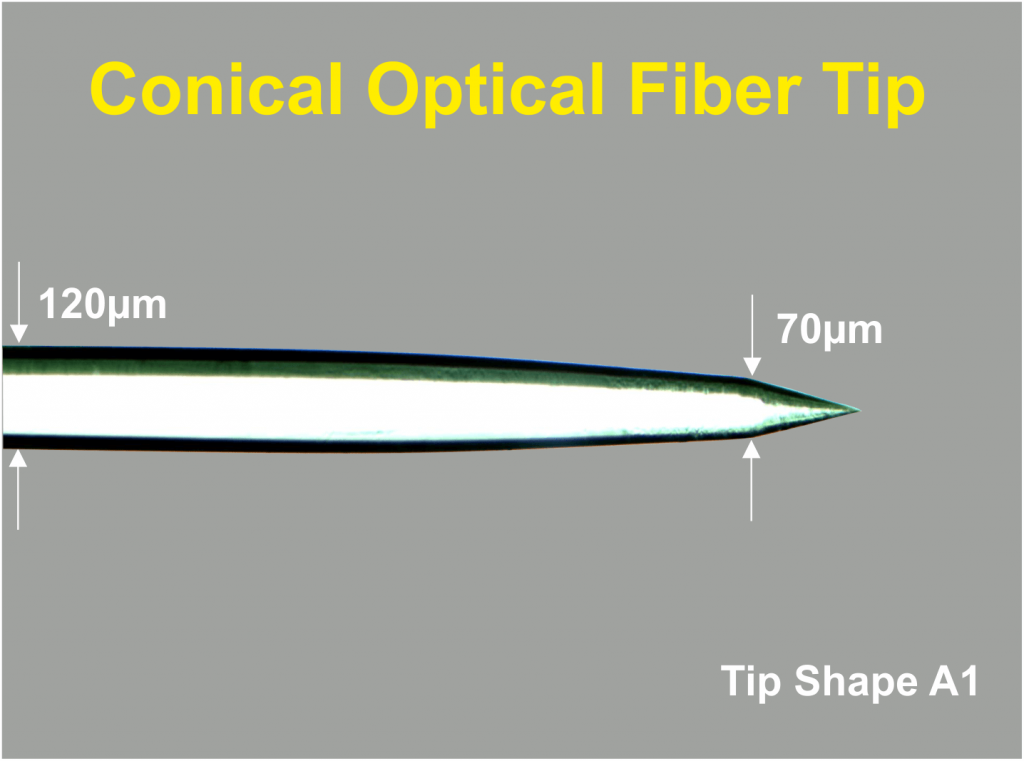
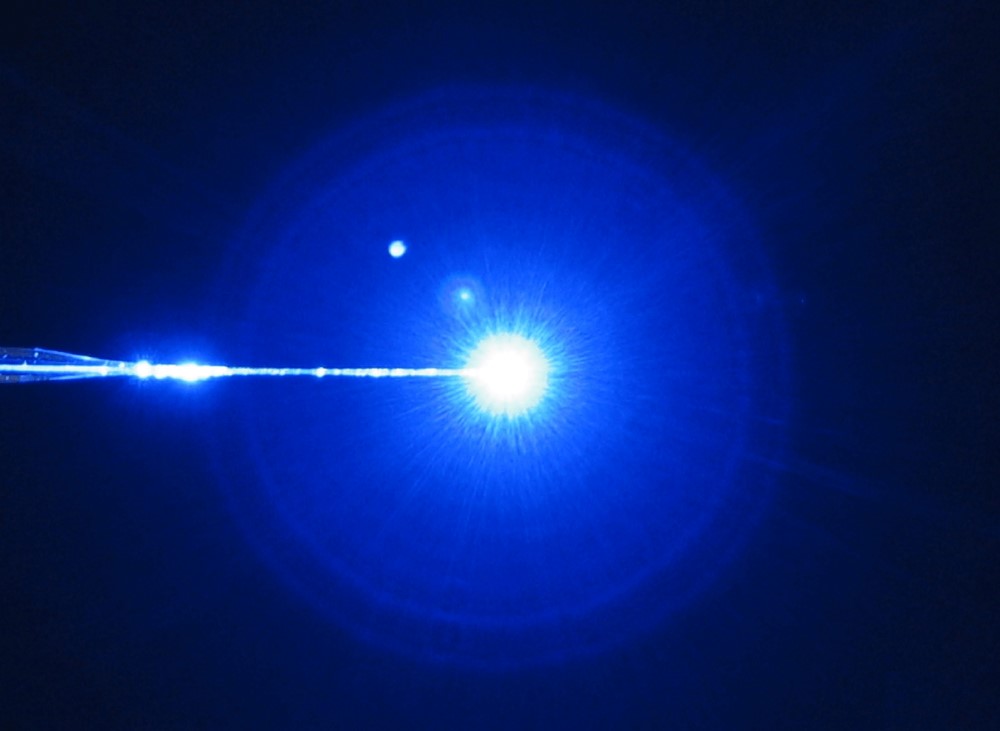
The advantage of Thomas conical and double conical fibers is that they do not cause tissue damage when introduced in brain tissue in comparison to blunt glass fiber tips. Furthermore Thomas Optical Fibers have a globular light distribution at the conical tip (see figure 4) in contrast to the cylindrical light distribution of blunt glass fibers.



Versatile
Thomas Optical Fibers are available for use in Thomas Microdrive systems (e.g. Mini Matrix, Eckhorn Matrix, see figure 5) and also for use with other manipulators (see figure 6).






Downloads
Publications
[3] Klein C., Evrard H. C., Shapcott K. A., Haverkamp S., Logothetis N. K., Schmid M. C. Cell-Targeted Optogenetics and Electrical Microstimulation Reveal the Primate Koniocellular Projection to Supra-granular Visual Cortex. Neuron Volume 90 Issue 1 Pages 143-151, April 2016, DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.02.036
[2] Stauffer W. R., Lak A., Yang A., Borel M., Paulsen O., Boyden E. S., Schultz W. Dopamine Neuron-Specific Optogenetic Stimulation in Rhesus Macaques. Cell 166, 1564-1571, September 2016, DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.024
[1] Kruse W., Krause M., Aarse J., Mark M. D. , Manahan-Vaughan D., Herlitze S.: Optogenetic Modulation and Multi-Electrode Analysis of Cerebellar Networks In Vivo PLOS ONE 9(8): e105589, 2014, DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105589
Questions? Please don’t hesitate contacting us!



NEWS


PRODUCTS



SOLUTIONS



DISTRIBUTORS
SIGN UP TO OUR NEWSLETTER